Bunions most often form on the inside of the foot at the big toe joint, but they can also develop on the outside of the foot at the base of the little toe. This smaller bunion is often referred to as a bunionette. In both cases, the affected toe is pushed against the other toes, creating a bony bulge.
Heredity is the largest factor in the formation of bunions, but shoe gear can both accelerate and exacerbate the condition. Arthritis and misalignments in the bone structure of the foot can also cause bunions to form as well. Some bunions get bigger quickly while other bunions grow over a period of years. Bunions affect men and women, although they are more commonly symptomatic in women. This is likely due to shoe gear.
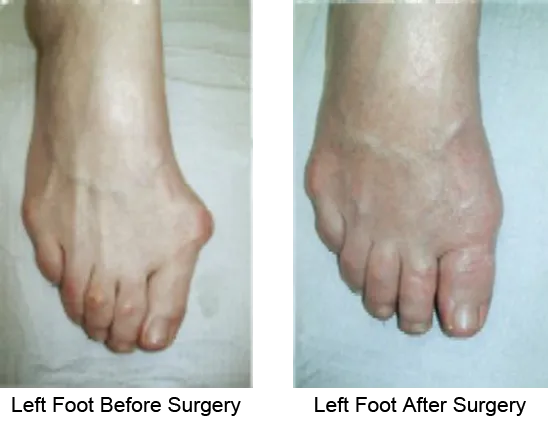
Symptoms of a bunion include joint soreness, pain and swelling. The amount of pain does not always relate to the size of the bunion; small bunions can be very painful while larger bunions can cause only minor discomfort or no pain at all. Left untreated, bunions can cause the toes to overlap and rub together; this leads to the development of heavy calluses, increased pain and tissue breakdown.
Treatment options vary depending on the size of the bunion and severity of pain. Conservative options range from wearing properly fitted shoes with a wide toe box, orthotics and wearing bunion shields during the day or bunion splints at night to relieve pressure. If you experience increasing pain, pain at the ball of the foot or difficulty walking, your doctor may recommend outpatient surgery to realign the bone.

